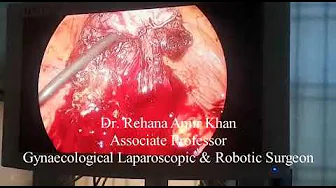
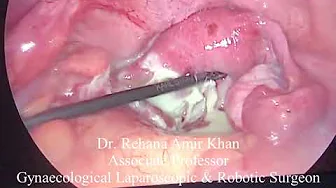
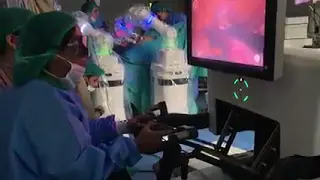
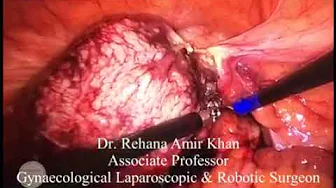
Laparoscopic Tubal Reconstructive Surgery
LAPAROSCOPIC TUBAL RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY
Consult the Best Gynecological Laparoscopic Surgeon in Lahore.
With years of experience in Gynecology, we are here to help
Our Specialist Gynecological Laparoscopic surgeons are specialized in all kinds of:
Laparoscopic Tubal Reconstructive Surgery
Sterilization is a permanent method of birth control for women who do not want to become pregnant in the future. The laparoscopic technique is a minimally invasive procedure, and laparoscopic sterilization has gained popularity in recent years due to its advantages over traditional methods. Laparoscopic sterilization is a tubal ligation technique to block or close the fallopian tubes, which are the way sperm travel to the egg for fertilization.
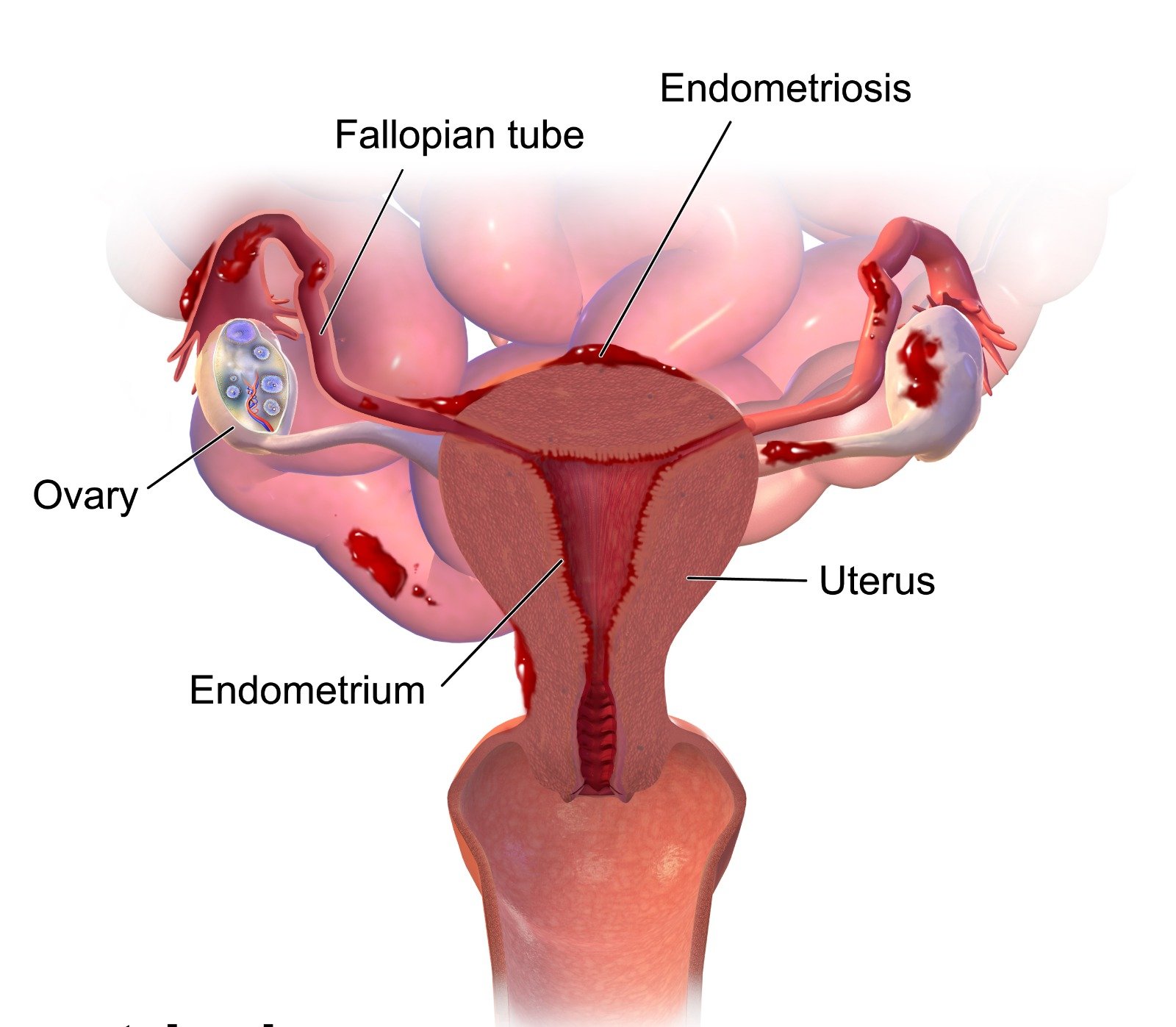
The fallopian tubes, located on either side of the uterus, collect the eggs released by the ovaries and transport them to the uterus. If these ducts are blocked, sperm cannot reach the egg and fertilization cannot occur.
Laparoscopic Tubal Reconstructive Surgery also refers to reversal sterilization which is a surgical procedure that restores fertility by restoring normal function to the fallopian tubes that were blocked during sterilization. About 5-10% of women may need to reverse sterilization for various reasons, such as having a new partner and wanting more children. Women who have their tubes removed during sterilization cannot be reversed.
Why you should go for Laparoscopic Tubal Reconstruction Surgery?
The main reason women want to have tubal reconstruction surgery is to restore fertility. With tubal ligation (female sterilization, in which the fallopian tubes are cut and tied or closed), pregnancy is not possible. This procedure can reverse the tubal ligation back to its original state so you can get pregnant again.
What is Laparoscopic Tubal Reconstruction?
Laparoscopic tubal reconstruction is performed under general anesthesia. Moreover, a tiny incision is made in the abdomen to insert the laparoscope. The fallopian tubes are assessed, and the separate ends of the fallopian tubes are refreshed and sutured together.
LAPAROSCOPIC TUBAL RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY
Factors Affecting Tubal Reconstructive Surgery
The main factors that affect the results of inversion after sterilization are as follows:
Age
Generally, tubal reconstruction is a good option for women under the age of 35. After this, the age of the mother becomes another infertility issue. Most women over the age of 35 are more successful with IVF.
Previous tubal ligation
Women who have had their fallopian tubes ligated before are usually good candidates for deconstruction and reconstruction. Likewise, we will need to look at the ligation method used and determine if any other injuries might make the reconstruction less effective.
Endometriosis, pelvic infection, and previous surgery
Endometriosis, pelvic infection, and previous surgery can cause scarring that can block one or both tubes. These conditions can lead to adhesion around the tube and displace them from their normal position. With laparoscopic surgery all the adhesion around the tube are broken with special equipment, and position of the tube is restored. This procedure will restore your fertility but is only ineffective if disease is very severe and has lead to distortion of the length of the tube.
Understand the risks
All patients should understand the risks associated with any infertility treatment. Reconstruction of the fallopian tubes with reverse ligation has the highest success rate at 80%. However, reconstruction success rates for tubal reconstruction secondary to endometriosis, PID, and previous surgery are variable, ranging from 10% to 60% depending upon the level of expertise of laparoscopic surgeon and severity of disease. Women who choose to undergo tubal reconstruction should have a thorough understanding of the risks involved. If reconstruction is unsuccessful, in vitro fertilization can be performed later.
Before surgery, patients should undergo tests that include:

LAPAROSCOPIC TUBAL RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY
Laparoscopic Tubal Reconstructive Procedure
Cancellation after sterilization is a safe procedure that includes the following steps:
Postoperative care
The procedure can take several hours, and patients are usually discharged the same day as the procedure within 24 hours. Patients are advised to follow the instructions of their surgeon, as well as the recommended diet and prescription medications. For a few days after surgery, the patient can carry out daily activities such as driving, walking, etc. It may take a few days to a few weeks for patients to fully recover.
Risks and Complications
Possible risks associated with reverse sterilization include:
LAPAROSCOPIC TUBAL RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY
What is the recovery time for laparoscopic tubal reconstruction?
How long it takes to fully recover depends on the type of surgery you had. After laparoscopy, usually takes about a week.
Can tubal reconstruction cause weight gain?
Since tubal reconstruction does not affect hormones or appetite, it does not cause weight gain. Although microsurgery can reconnect the tubes, restoration of fertility is not guaranteed. Pregnancy rates after female sterilization reversal range from 30% to 80%.
Still confused about the Tubal Reconstruction Surgery
Candidates for Laparoscopic tubal reconstruction are women of reproductive age when other causes of sub fertility have also been addressed. In most cases, these women are healthy and only need a complete blood count and blood test before surgery. The preoperative evaluation depends on the patient's medical history and needs. Moreover, the use of prophylactic perioperative antibiotics to prevent infection and the use of corticosteroids or antiprostaglandin drugs, high berry gel and other pharmacological gels to reduce adhesion formation.
LAPAROSCOPIC TUBAL RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY
Consult With Our Expert Gynecological Surgeon in Lahore
Our goal is to help every couple realize their dream of having a family. Our Laparoscopic surgeon in Lahore carefully screen all options for fertility to address all concerns and increase the chances of pregnancy.
Feel free to discuss infertility treatment with best Gynecologist in Lahore, please contact us any minute, and you will receive guaranteed results.
Complete recovery after LAPAROSCOPIC TUBAL RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY takes about two to four weeks when you will get rid of vaginal discharge and spotting and can contact your doctor for resuming sexual activity. Recovery from an abdominal hysterectomy can take up to six weeks. Talk to your healthcare provider before you go home to make sure you know the best way to take care of yourself.
It is normal to experience bloating or gas after a hysterectomy. It may take several weeks for abdominal puffiness and swelling to subside. Talk to your healthcare provider about ways to reduce discomfort. Some exercise, heat packs, or dietary changes may help.
It depends on whether the ovaries have been removed. If your ovaries are still there after a hysterectomy, you won't go into menopause right away. If both ovaries are removed during a hysterectomy, you may go into menopause right away.
Generally, no, especially if you are considered to be at low risk of cervical cancer. If you have had a hysterectomy for cancer, you should continue to have a Pap test.