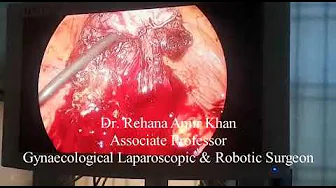
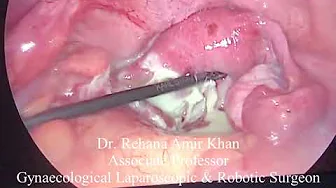
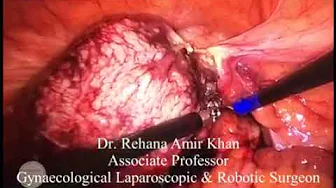
Treatment of Septum

TREATMENT OF SEPTUM
Consult the Best Gynecological Laparoscopic Surgeon in Lahore.
With years of experience in Gynecology, we are here to help
Our Specialist Gynecological Laparoscopic surgeons are specialized in all kinds of:
Congenital vaginal and uterine Problems
Congenital malformations of the vagina and uterus are developmental problems that develop in the fetus. The common orangs where these can occur are in the vagina, ovaries, uterus, or cervix.
When you should visit us?
While some congenital abnormalities of the vagina and uterus may be asymptomatic, common symptoms include:
Are you facing
Then you might experience vaginal septum; visit the best Gynecologist in Lahore for an authentic checkup.
TREATMENT OF SEPTUM
Need To Know About Vaginal Septum
A vaginal septum is a congenital abnormality of the vagina; it is present at birth. This abnormality is formed in the reproductive system during fetal development, while the baby is included in the mother's womb.
In more simple words, a partition that separates two rooms. The presence of a vaginal septum means that a piece of tissue formed during fetal development divides the vagina in two. This part can interfere with menstrual, sexual function, and childbirth.
Different types of Septums
Vaginal septums are classified according to how the septum is formed and placed. We use the following terms to describe the different formations of the vaginal septum: lateral or longitudinal (whether the septum passes through the vagina or longitudinal), obstructive or non-obstructive (whether the septum prevents menstrual flow), high or low (the thickness of the vaginal septum at the location), and Thin or thick (the consistency of the septum tissue).
Longitudinal Vaginal septum
The septum runs along the length of the vagina and divides the vagina into two ducts. This type of barrier does not block menstruation.
Vaginal Halves Obstruction
Part of the septum separates and blocks half of the vagina, which is almost always associated with bilateral (bi) uterine and renal (kidney-related) abnormalities on the same mass side. Girls with this vaginal anomaly have regular periods on one side and blocked periods on the other.
Transvaginal septum
The septum passes through the vagina and can be low, mid, or high. An intact transverse vaginal septum blocks the vagina and impedes menstrual flow. A perforated transverse vaginal septum only partially blocks the vagina and contains an opening that allows menstruation to pass.
TREATMENT OF SEPTUM
Causes of vaginal septum
Doctors don't fully understand the causes of vaginal abnormalities. They are considered multifactorial, likely caused by defects in multiple genes, with some influence from our environmental factors.
A woman's reproductive organs begin to develop in the mother's womb or the womb at about six weeks of pregnancy (six weeks after conception). It mostly happens when two Müllerian ducts slowly migrate to the embryo, then fuse in the middle. Some tissue migrates up to form the uterus and fallopian tubes, while the rest migrates down to form part of the vagina.
The Müllerian duct fuses with the vaginal plate, forming the vaginal canal. However, any disturbance in this process can cause the uterus or vagina to deform. Plus, these types of anomalies are called Mueller anomalies.
Chances of the vaginal septum in women
A vaginal septum is a congenital anomaly that can occur in any woman. Doctors have not identified any specific risk factors for this condition. Vaginal malformations can be isolated or associated with other abnormalities, including renal malformations, skeletal malformations, or anal malformations related to the anus or rectum.
TREATMENT OF SEPTUM
Signs and symptoms of a vaginal septum
Longitudinal Vaginal Septum
Some girls with this type of septum have a normal uterus, but most also have Müllerian duct abnormalities, such as a single uterus or both. People with mediastinum have regular menstrual periods (periods), but they may report difficulty using tampons or pain during intercourse. Sometimes, a woman has no symptoms, and a doctor finds a vaginal septum during a routine pelvic exam.
Transvaginal septum
In the case of an intact transverse vaginal septum, menstrual blood flow is blocked, causing swelling of the upper vagina and uterus. Patients with these abnormalities experience amenorrhea (irregular periods), increased recurring pelvic pain, and sometimes a lump in the abdomen, a blood-filled uterus. Patients may experience no symptoms when the vaginal septum is punctured. Or, they may find it difficult to use tampons and experience painful intercourse.
Vaginal Hemisphere Obstruction
Obstruction of both halves of the vagina is almost always associated with uterine unevenness and kidney abnormalities on the same side of the block. Girls with this type of septum menstruate normally but exacerbate periodic pelvic pain.
Diagnostic Test For Vaginal Septum.
We diagnose the vaginal septum by performing pelvic exams and imaging tests using a 3D ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machine.
Ultrasound uses sound waves to create images of the inside of the abdomen and pelvis, while MRI uses magnets to create images of internal structures and organs.
Sometimes the vaginal septum is associated with skeletal or urinary tract abnormalities, so further X-rays and kidney imaging may be required.
An internal pelvic exam is a complete physical examination of the pelvic structures. We recommend doing this while the patient sleeps under sedation to minimize inconvenience.
Why choose us for these imaging tests?
A vaginal septum is rare and must be appropriately diagnosed before surgery is considered. Since these conditions are rare, radiologists must be aware of these abnormalities, so it is essential to go to the hospital with an experienced radiology team.
Because we are expert gynecologist surgeons over the past decade, our radiologists have the training and experience to diagnose these conditions accurately.
How do we diagnose uterine abnormalities?
After the imaging tests, your doctor will review this information along with your medical history and pelvic exam to make a diagnosis.
Treatment of vaginal septum
Surgical removal or removal of septum tissue is the most definitive way to treat complications related to the vaginal septum. However, the surgery's timing depends on the septum's symptoms and characteristics. Asymptomatic women, usually those with a non-obstructing septum, do not necessarily require intervention. But it's important to note that this barrier can interfere with tampon use, sex, and childbirth so that surgery can be done later for comfortable tampon use, sex, and safe vaginal delivery.
TREATMENT OF SEPTUM
Uterine Septum(bicornuate uterus)
If you are experiencing:
You must visit us if you are facing any difficulty.
The following tests we take to diagnose a bicornuate uterus:
TREATMENT OF SEPTUM
Need To Know About Bicornuate Uterus
A bicornuate uterus occurs when a woman's uterus is heart-shaped. For this reason, this condition is sometimes referred to as a "heart-shaped uterus."
The uterus in a woman is the organ where a fertilized egg grows and develops into a child.
The shape of a woman's uterus is essential when she is trying to conceive and during pregnancy.
A woman with a bicornuate uterus may find her baby lying in an irregular position, which may interfere with delivery.
It is not known whether a bicornuate uterus affects fertility. The only treatment for this condition is surgery to correct the shape. Other types of abnormalities can also affect a woman's uterus.
If you have frequent miscarriages, then you must go for a check-up.
It is difficult to pinpoint exact figures for the increased risk of miscarriage and preterm birth. The vast difference in these numbers makes it difficult for women to know their chances of miscarriage.
Women with a bicornuate uterus have a higher chance of having a baby with congenital disabilities than women with a normal-shaped uterus.
One study reported that children born to women with bicornuate uterus had four times the risk of congenital disabilities compared to women without the condition.
If a woman with a bicornuate uterus becomes pregnant, her condition is considered high risk. This means more frequent monitoring of pregnancies, increased checks on the baby's health and development, early detection of any problems, and reduced risk.
Cesarean delivery might be necessary if the baby was in a breech position before birth.
Other uterine abnormalities
Some other uterine abnormalities include:
Septate uterus
This is where a group of muscles or tissue called the diaphragm divides the uterus. This can lead to repeated miscarriages in women. Surgery to repair the uterus is usually recommended.
Unicornuate Uterus
It is also called a unilateral uterus. This is a uterine malformation in which only half of the uterus is formed.
Symptoms of Bicornuate Uterus
A bicornuate uterus usually doesn't cause any symptoms, which may mean it's undiagnosed.
About 3% of women have an irregular uterus. The irregularity can be the uterus's size, structure, or shape. One of the most common types of abnormalities is a bicornuate uterus.
Often, women are born with a bicornuate uterus but may not realize it because there are no other symptoms or symptoms that do not feel anything unusual. Many women find out they have the disorder only after an ultrasound or imaging test.
However, women with bicornuate uterus may experience any of the following accompanying symptoms:
Causes of Bicornuate Uterus
A woman's womb grows in her mother's womb. Uterine defects may occur if her uterus is not developing correctly. This is called a congenital malformation, and women are born with the condition. It is impossible to prevent or prevent this from happening.
A bicornuate uterus is caused by abnormal development of the ducts adjacent to the kidneys.
When the ducts fail to fuse correctly, the uterus splits into two bulges, creating a heart-shaped appearance.
Diagnosis of Bicornuate Uterus
A bicornuate uterus can be diagnosed after ultrasonography. Because of the subtlety of symptoms, a woman with a bicornuate uterus may not know she has the condition until she has an ultrasound during pregnancy or for other reasons. Sometimes, it may never be discovered.
Treatment and Surgery
Treatment of bicornuate uterus is resection of the septum on hysteroscopy. With the help of telescope through vagina without any incision, special equipment is inserted inside the uterine cavity for break down and resolution of the septum. It is recommended if woman is not getting pregnant with bicornuate uterus .
This procedure may also be recommended if a woman has repeated miscarriages and the cause is thought to be a bicornuate uterus.
TREATMENT OF SEPTUM
Absent Vagina
Vaginal Abnormalities: Absent Vagina (Vaginal Agenesis/Hypoplasia)
Vaginal hypoplasia or Absent Vagina is a congenital disability that affects a small number of women (1 in 5,000). But unless it's fixed, it makes it impossible to have sex and have children. It occurs when the vagina is not fully developed. Some girls may have a shorter vagina, residual vagina, or none. It is not uncommon to have other problems with the reproductive system, such as a missing uterus or a uterus that is too small.
Additionally, 30 out of every 100 girls with vaginismus have kidney abnormalities. The most common is the loss of a kidney or the dislocation of one or both organs. The kidneys can also attach, forming a horseshoe shape. About 12 in 100 women have atypical bones, and two-thirds of women in this group have problems with the spine, ribs, or limbs.
Symptoms of Absent Vagina or Vagina Agenssis
Symptoms of vaginitis are associated with a condition called amenorrhea. Amenorrhea is the absence of menstruation after puberty begins.
Because the vagina has not formed, girls with amenorrhea can grow normally. However, they may encounter the following situations:
Possible Reason for Absent Vagina
The reason why the vagina does not form is not fully understood.
Some believe the condition is caused by the failure of specific organs (Müllerian ducts) formed during fetal development.
How do we diagnose it?
Because external genitalia appears normal, they are usually not discovered until around age 15, when the girl notices that she has not come and seeks medical attention. Diagnosis relies on physical examination and imaging studies. Ultrasound can be used to examine the uterus and ovaries. If necessary, MRI can show a complete picture of the reproductive system.
Most girls don't know about the problem until their teens. But some cases can be found in childhood, usually during testing or testing for other issues.
Vagina Agenesis Treatment
Many people ask when girls should consider creating a vagina. But when the process begins, it's up to her. Most girls start therapy in their teens, but some may want to wait until they're ready to have sex.
Self-expansion
Some girls can have vaginas without surgery. A tiny tube (called a dilator) is pressed against the skin where the vagina should be located for 15 to 20 minutes a day. This is easiest after a shower as the skin is soft and stretched well. This is best for girls with dimples in the area.
Laparoscopic Vaginoplasty
Most young women will need surgery, and how it is done can vary. Vaginal transplants can be done through the skin or buccal mucosa (the lining of the cheeks) or form part of the large intestine. Vaginal transplants have their own side effects of secretions and narrowing, better is to go for laparoscopic formation of vagina in which no transplant are graft is used and absent vagina is recovered in its normal form. We, as expert gynecologist surgeon in Lahore, thoroughly recommend surgery when the upper part of the vagina can descend into the area that should be the standard vaginal opening. This is called " Laparoscopic vaginoplasty."
Through this, an average vagina is created. The swollen tissue with blood at the top of the vagina is stretched. So that the upper part of the vagina can now reach the lower part of the vagina. Once an average vagina has formed, you may need to use a vaginal dilator to reduce the risk of surrounding scar tissue forming. Once corrected, affected women should have normal reproductive function and fertility.
Common Queries After Surgery
Although you should talk to your healthcare provider before having sex, starting 4 to 6 weeks after treatment is usually a good idea. Lubrication may be required because the skin does not produce the same material as normal vaginal tissue.
Since most of your sexual pleasure comes from stimulating the clitoris (the female erectile structure) rather than the vagina, you should enjoy normal sensations and good sex life. Because these changes are internal, no one can tell you that you received treatment.
Your anatomy will be the most critical factor in determining whether you will be able to have children. You will likely be pregnant if your uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes are normal. If you have a small or no uterus, you are less likely to get pregnant on your own. However, if your ovaries are healthy, you can have IVF with a surrogacy specialist.
Don't worry about anything, because you are in good hands.
All Congenital vaginal and uterine Problems are rare and require management by an experienced multidisciplinary care team. We have the expertise to manage complex cases and teams to improve surgical outcomes and patient well-being.