Molar Pregnancy
TREATMENT OF MOLAR PREGNANCY
If You Think You Are Experiencing Symptoms Or Are Experiencing A Molar Pregnancy,
Or, If You Have Questions About It, Talk To Our Expert Gynecologist In Lahore.
Need To Know About Molar pregnancy
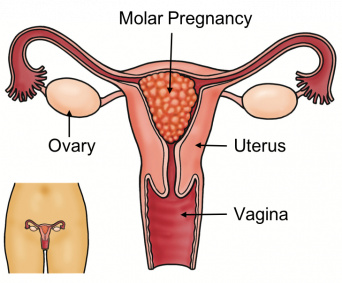
A molar pregnancy occurs when the tissue surrounding the fertilized egg develops abnormally. It is also known as a Hydatidiform mole, a rare pregnancy complication that happens by abnormal growth of trophoblasts (the cells that usually grow into the placenta). You may experience any one of these types:
Partial molar pregnancy
In addition to abnormal tissue, some normal pregnancy tissue, such as the fetus, amniotic tissue, or umbilical cord, is present. If the fetus grows, it usually dies early in pregnancy due to this condition. In some molar pregnancies, the fetus rarely survives to term.
Complete molar pregnancy:
In this form of molar pregnancy, normal pregnancy tissue does not develop. The cause of a molar pregnancy is related to problems with exchanging genetic information for the egg or sperm.
TREATMENT OF MOLAR PREGNANCY
Difference Between Normal Pregnancy and Molar Pregnancy
During a normal pregnancy, an egg and sperm fuse (fertilize) and share their genetic material. In a complete molar pregnancy, sperm cells fertilize an egg without genetic material. The fertilized egg usually dies at this stage, but in rare cases, it implants in the uterus and causes an abnormal pregnancy.
A partial molar pregnancy occurs when two sperm fertilize an egg. In this case, there is a lot of genetic material, and the pregnancy can develop abnormally.
This condition is usually benign (not cancerous). However, if the molar pregnancy is not removed, it can become cancerous. A complete molar pregnancy is more likely to develop molar cancer than a partial molar pregnancy.
TREATMENT OF MOLAR PREGNANCY
Symptoms Of Molar Pregnancy
A woman with a molar pregnancy has a positive pregnancy test and early symptoms as in a normal pregnancy. Pregnancy may appear normal for the first three to four months without medical intervention or diagnosis.
However, some signs and symptoms of molar pregnancy are:
Talk to our Gynaecologist if you have any signs or symptoms of a molar pregnancy. It may detect other signs of a molar pregnancy, such as:
TREATMENT OF MOLAR PREGNANCY
Reasons Why Molar Pregnancy Happens?
An abnormally fertilized egg is the leading cause of molar pregnancy. In general, a human body has 23 pairs of chromosomes. Where each pair of chromosomes comes from the father and the other from the mother. In a complete molar pregnancy, the empty egg is fertilized by one or two sperm, and all the genetic material comes from the father. In this case, the chromosomes from the mother's egg are missing or malfunctioning, and the father's chromosomes are doubled.
The mother's chromosomes are still present in a partial or incomplete molar pregnancy, but the father provides both sets. As a result, the fetus has 69 chromosomes instead of 46. It happens when two sperm fertilize an egg, producing a different replica of the father's genetic material.
TREATMENT OF MOLAR PREGNANCY
Risk factors in Molar Pregnancy
About 1 in 1,000 pregnancies is diagnosed as a molar pregnancy. Several factors are associated with a molar pregnancy, including:
Complications In Molar Pregnancy
After the molar pregnancy is removed, molar tissue may remain and continue to grow. This is called a persistent gestational trophoblastic tumor (GTN).
A hallmark of persistent GTN has elevated levels of human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG), a pregnancy hormone removed after a molar pregnancy. In some cases, an invasive mole penetrates the middle layer of the uterine wall, causing vaginal bleeding.
Molar Pregnancy Diagnosis
Blood and urine tests detect abnormally high human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG), which may indicate a molar pregnancy.
Other tests may be done to check for preeclampsia and hyperthyroidism.
It is most often detected with an ultrasound scan during the first trimester.
Treatment For Molar Pregnancy
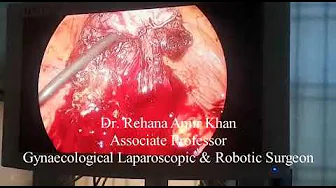
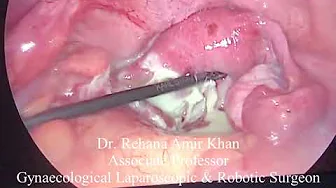
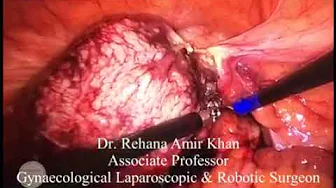
Treatment usually involves curettage (D&C) to remove molar tissue in the uterus, which, if not removed, has a low risk of cancer.
In most cases, undiagnosed molar pregnancies result in spontaneous abortion in the fourth month of pregnancy. D&C can also use vacuum aspiration (suction) to remove molar tissue. D&C is a minor procedure performed under general anesthesia.
More likely, if a molar pregnancy is diagnosed before the miscarriage.
Persistent GTN can almost always be treated successfully, usually with chemotherapy. Another treatment option is to remove the uterus (hysterectomy).
Rarely a cancerous form of GTN called choriocarcinoma develops and spreads to other organs. Placental cancer can often be successfully treated with several anticancer drugs. These complications are more common in a complete molar pregnancy than in a partial molar pregnancy.
Precautions To Avoid Molar Pregnancy
If you have had a molar pregnancy, talk to a doctor or gynecologist before getting pregnant again. A doctor will recommend waiting for six months or a year before trying to conceive. The risk of recurrence is low but higher than in women without a history of molar pregnancy.
Our doctor may perform an early ultrasound during any subsequent pregnancy to monitor your condition and ensure average growth. Our doctor also discusses prenatal genetic testing, which can be used to diagnose a molar pregnancy.
TREATMENT OF MOLAR PREGNANCY
Consult our Expert Laparoscopic Gynaecologist Surgeons For Quick Consultation
Follow-up Session After Molar Pregnancy Treatment
Treatment is usually successful. However, there is a small risk of abnormal molar cells in the uterus continuing to grow or become cancer, follow-up is generally required for 2 to 12 months.
Regular blood tests are done to monitor the drop in HCG levels. Elevated HCG levels after pregnancy may indicate that not all molar tissue has been removed or that cancer is developing due to molar pregnancy.
While the condition is under control, it is essential to avoid pregnancy. This can be as long as a year, although the recommendations for each woman will vary.
Do not worry about anything; you are in good hands.
TREATMENT OF MOLAR PREGNANCY
We are the expert Gynecologist in Lahore; we provide the best pregnancy care. We assure you we treat you with state of the art services with all our ability to make your life happy.