Bartholin Cyst
TREATMENT OF BARTHOLIN CYST
Need To Know About Bartholin Cyst
Bartholin's glands are a pair of small glands located next to the lower part of the vaginal entrance. The gland is about 1 cm in diameter or the size of a pea. Unless you are infected, you usually cannot see or feel these glands because they are located in the soft tissue (labia) next to the entrance to the vagina. Each gland produces a small amount of mucus. This helps keep the vaginal entrance moist.
Discuss your issue with expert gynecologist in Lahore for a quick consultation and world-class treatment.
What is a Bartholin abscess?
Bartholin's glands are located at the entrance to the vagina and secrete mucus. The ducts leading to these glands can block, causing swellings called cysts. It is unclear what causes the blockage of the ducts that cause these cysts. Suppose the cyst becomes infected, and an abscess containing pus forms. Cysts can be three times as common as cysts.
Symptom for Bartholin Cyst
It's kind of relaxed that Bartholin's cysts have no major symptoms and are painless. However, if an infection develops and an abscess develops, symptoms may include:
TREATMENT OF BARTHOLIN CYST
How common are Bartholin's cysts/abscesses?
About 2% of women will have a Bartholin cyst at some point. This condition usually affects sexually active women between 20 and 30.
Diagnosis of Bartholin cyst
Typical appearance of a Bartholin cyst/abscess; therefore, a doctor's examination can often diagnose the problem. Usually, no tests are required to make a diagnosis.
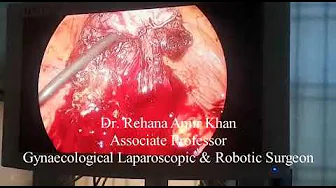
Treatment of Bartholin Cyst
Most treatments involve minor surgical procedures performed under local or general anesthesia.
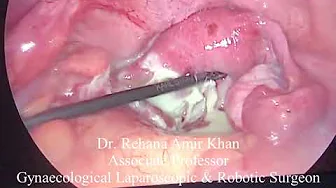
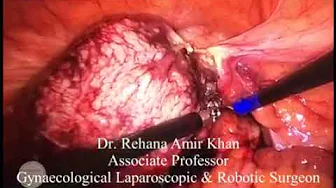
The surgical incision under general anesthesia
A minor procedure called sedation is performed while you sleep under general anesthesia. A small surgical incision on the abscess will allow the gland to drain freely. The incision is enlarged to about 1 cm, and the inner layer of the cyst is sutured with a few stitches, covering it with skin. This will create a new permanent opening for fluid to drain from the gland. The stitches used will be dissolvable. This provides excellent relief and usually results in a quick recovery.
The average hospital stay is between 12 and 24 hours, and everyday activities can usually be resumed within two to three days, although discomfort may last longer than this.
It will take you about two weeks to fully recover. Abscesses are usually treated permanently but sometimes recur later. Depending on the procedure used, up to 38% develop an abscess later in life but not in first few years after surgery.
Catheter insertion under local anesthesia
Inserting a "word catheter" is a minimally invasive procedure that can be performed under local anesthesia in an emergency gynecological unit (EGU). A chevron catheter is a thin, flexible rubber tube with a small, specially designed balloon at the tip.
A small incision is made in the abscess, the tip of the catheter is inserted, the balloon is inflated with fluid, and the incision is partially closed with sutures to help hold the balloon in place. It is then left for up to four weeks to allow new skin to form around the channel and enable the wound to heal.
A follow-up appointment will be scheduled for the EGU; after that, the balloon will be deflated and removed, allowing the gland to drain through the newly formed channel.
TREATMENT OF BARTHOLIN CYST
Aftercare
After surgery, you may be prescribed antibiotics, but this is not always required. You may experience discomfort and tingling at the surgery site. A warm bath can relieve these symptoms, as well as simple pain relievers (pain relief) you can buy over the counter.
You may experience some discharge at the incision site, which is normal and may last for a few days. Bathing or showering once or twice a day is recommended to aid healing. It is generally recommended to avoid intercourse until the area has healed and is no longer painful.
You can return to work when you feel able to resume normal activities.
Book your appointment today with the expert Laparoscopic surgeon in Lahore.
No follow-up appointment will be arranged after catheterization is completed.
It has been removed, so don't hesitate to get in touch with your doctor if you have any questions.
We are the expert gynecological Laparoscopic Surgeon in Lahore; who provide the treatment and care you deserve with advanced technologies.